Exclusion Constraint Dialog¶
Use the Exclusion constraint dialog to define or modify the behavior of an exclusion constraint. An exclusion constraint guarantees that if any two rows are compared on the specified column or expression (using the specified operator), at least one of the operator comparisons will return false or null.
The Exclusion constraint dialog organizes the development of an exclusion constraint through the following dialog tabs: General, Definition, and Columns. The SQL tab displays the SQL code generated by dialog selections.
Use the fields in the General tab to identify the exclusion constraint:
Use the Name field to provide a descriptive name for the exclusion constraint. The name will be displayed in the pgAdmin tree control.
Click the Definition tab to continue.

Use the fields in the Definition tab to define the exclusion constraint:
Use the drop-down listbox next to Tablespace to select the tablespace in which the index associated with the exclude constraint will reside.
Use the drop-down listbox next to Access method to specify the type of index that will be used when implementing the exclusion constraint:
Select gist to specify a GiST index.
Select spgist to specify a space-partitioned GiST index.
Select btree to specify a B-tree index.
Select hash to specify a hash index.
Use the Fill Factor field to specify a fill factor for the table and associated index. The fill factor is a percentage between 10 and 100. 100 (complete packing) is the default.
Move the Deferrable? switch to the Yes position to specify that the timing of the constraint is deferrable, and can be postponed until the end of the statement. The default is No.
If enabled, move the Deferred? switch to the Yes position to specify the timing of the constraint is deferred to the end of the statement. The default is No.
Use the Constraint field to provide a condition that a row must satisfy to be included in the table.
Click the Columns tab to continue.
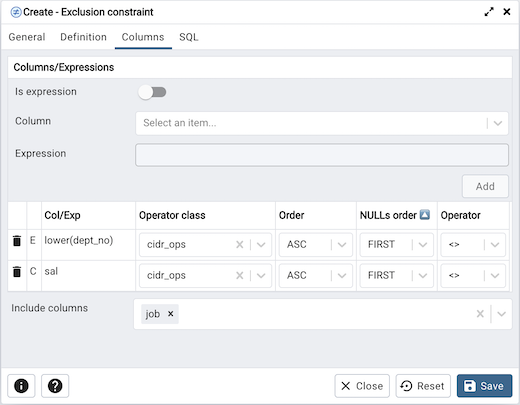
Use the fields in the Columns tab to specify the column(s) or expression(s) to which the constraint applies. Use the Is expression ? switch to enable expression text input. Use the drop-down listbox next to Column to select a column. Once the Column is selected or the Expression is entered then click the Add icon (+) to provide details of the action on the column/expression:
The Col/Exp field is populated with the selection made in the Column drop-down listbox or the Expression entered.
If applicable, use the drop-down listbox in the Operator class to specify the operator class that will be used by the index for the column.
Move the DESC switch to DESC to specify a descending sort order. The default is ASC which specifies an ascending sort order.
Use the NULLs order column to specify the placement of NULL values (when sorted). Specify FIRST or LAST.
Use the drop-down list next to Operator to specify a comparison or conditional operator.
Use Include columns field to specify columns for INCLUDE clause of the constraint. This option is available in Postgres 11 and later.
Click the SQL tab to continue.
Your entries in the Exclusion Constraint dialog generate a SQL command (see an example below). Use the SQL tab for review; revisit or switch tabs to make any changes to the SQL command.
Example¶
The following is an example of the sql command generated by user selections in the Exclusion Constraint dialog:
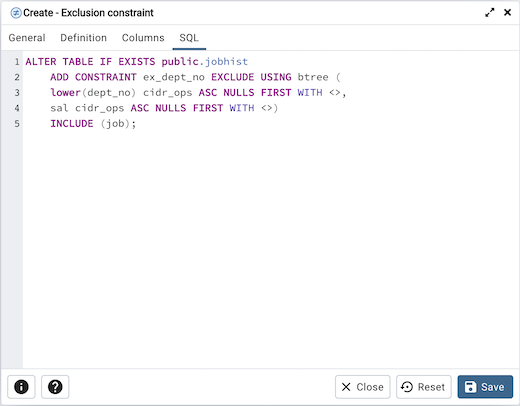
The example shown demonstrates creating an exclusion constraint named ex_dept_no. The constraint uses a btree index.
Click the Info button (i) to access online help.
Click the Save button to save work.
Click the Close button to exit without saving work.
Click the Reset button to restore configuration parameters.